
⇧「虎穴に入らずんば虎児を得ず」じゃないですが、当然リスクも付きものだわね...
sudo: source: command not foundって言われてもね...
どうやら、
⇧ 「/etc/sudoers」を編集すれば良いらしい。
編集するときは、
/etc/suders の修正には visudo というコマンドを利用します。
問題なければ、viと同様の操作で保存してやればいいです。 もし構文をミスっていた場合は以下のように怒られるので、e を押して修正してください、q を押したが最後2度と sudo が実行できなくなるのでご注意ください。
⇧「visudo」ってコマンドで行うらしい。viと同じ操作方法になるみたいです。
で、「WSL 2(Windows SubSystem for Linux 2)」の「Oracle Linux 8.7」の「/etc/sudoers」のファイル中身は以下のようになっていました。
## Sudoers allows particular users to run various commands as ## the root user, without needing the root password. ## ## Examples are provided at the bottom of the file for collections ## of related commands, which can then be delegated out to particular ## users or groups. ## ## This file must be edited with the 'visudo' command. ## Host Aliases ## Groups of machines. You may prefer to use hostnames (perhaps using ## wildcards for entire domains) or IP addresses instead. # Host_Alias FILESERVERS = fs1, fs2 # Host_Alias MAILSERVERS = smtp, smtp2 ## User Aliases ## These aren't often necessary, as you can use regular groups ## (ie, from files, LDAP, NIS, etc) in this file - just use %groupname ## rather than USERALIAS # User_Alias ADMINS = jsmith, mikem ## Command Aliases ## These are groups of related commands... ## Networking # Cmnd_Alias NETWORKING = /sbin/route, /sbin/ifconfig, /bin/ping, /sbin/dhclient, /usr/bin/net, /sbin/iptables, /usr/bin/rfcomm, /usr/bin/wvdial, /sbin/iwconfig, /sbin/mii-tool ## Installation and management of software # Cmnd_Alias SOFTWARE = /bin/rpm, /usr/bin/up2date, /usr/bin/yum ## Services # Cmnd_Alias SERVICES = /sbin/service, /sbin/chkconfig, /usr/bin/systemctl start, /usr/bin/systemctl stop, /usr/bin/systemctl reload, /usr/bin/systemctl restart, /usr/bin/systemctl status, /usr/bin/systemctl enable, /usr/bin/systemctl disable ## Updating the locate database # Cmnd_Alias LOCATE = /usr/bin/updatedb ## Storage # Cmnd_Alias STORAGE = /sbin/fdisk, /sbin/sfdisk, /sbin/parted, /sbin/partprobe, /bin/mount, /bin/umount ## Delegating permissions # Cmnd_Alias DELEGATING = /usr/sbin/visudo, /bin/chown, /bin/chmod, /bin/chgrp ## Processes # Cmnd_Alias PROCESSES = /bin/nice, /bin/kill, /usr/bin/kill, /usr/bin/killall ## Drivers # Cmnd_Alias DRIVERS = /sbin/modprobe # Defaults specification # # Refuse to run if unable to disable echo on the tty. Defaults !visiblepw # # Preserving HOME has security implications since many programs # use it when searching for configuration files. Note that HOME # is already set when the the env_reset option is enabled, so # this option is only effective for configurations where either # env_reset is disabled or HOME is present in the env_keep list. # Defaults always_set_home Defaults match_group_by_gid # Prior to version 1.8.15, groups listed in sudoers that were not # found in the system group database were passed to the group # plugin, if any. Starting with 1.8.15, only groups of the form # %:group are resolved via the group plugin by default. # We enable always_query_group_plugin to restore old behavior. # Disable this option for new behavior. Defaults always_query_group_plugin Defaults env_reset Defaults env_keep = "COLORS DISPLAY HOSTNAME HISTSIZE KDEDIR LS_COLORS" Defaults env_keep += "MAIL PS1 PS2 QTDIR USERNAME LANG LC_ADDRESS LC_CTYPE" Defaults env_keep += "LC_COLLATE LC_IDENTIFICATION LC_MEASUREMENT LC_MESSAGES" Defaults env_keep += "LC_MONETARY LC_NAME LC_NUMERIC LC_PAPER LC_TELEPHONE" Defaults env_keep += "LC_TIME LC_ALL LANGUAGE LINGUAS _XKB_CHARSET XAUTHORITY" # # Adding HOME to env_keep may enable a user to run unrestricted # commands via sudo. # # Defaults env_keep += "HOME" Defaults secure_path = /sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin ## Next comes the main part: which users can run what software on ## which machines (the sudoers file can be shared between multiple ## systems). ## Syntax: ## ## user MACHINE=COMMANDS ## ## The COMMANDS section may have other options added to it. ## ## Allow root to run any commands anywhere root ALL=(ALL) ALL ## Allows members of the 'sys' group to run networking, software, ## service management apps and more. # %sys ALL = NETWORKING, SOFTWARE, SERVICES, STORAGE, DELEGATING, PROCESSES, LOCATE, DRIVERS ## Allows people in group wheel to run all commands %wheel ALL=(ALL) ALL ## Same thing without a password # %wheel ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL ## Allows members of the users group to mount and unmount the ## cdrom as root # %users ALL=/sbin/mount /mnt/cdrom, /sbin/umount /mnt/cdrom ## Allows members of the users group to shutdown this system # %users localhost=/sbin/shutdown -h now ## Read drop-in files from /etc/sudoers.d (the # here does not mean a comment) #includedir /etc/sudoers.d
以下のように編集しました。
## Sudoers allows particular users to run various commands as ## the root user, without needing the root password. ## ## Examples are provided at the bottom of the file for collections ## of related commands, which can then be delegated out to particular ## users or groups. ## ## This file must be edited with the 'visudo' command. ## Host Aliases ## Groups of machines. You may prefer to use hostnames (perhaps using ## wildcards for entire domains) or IP addresses instead. # Host_Alias FILESERVERS = fs1, fs2 # Host_Alias MAILSERVERS = smtp, smtp2 ## User Aliases ## These aren't often necessary, as you can use regular groups ## (ie, from files, LDAP, NIS, etc) in this file - just use %groupname ## rather than USERALIAS # User_Alias ADMINS = jsmith, mikem ## Command Aliases ## These are groups of related commands... ## Networking # Cmnd_Alias NETWORKING = /sbin/route, /sbin/ifconfig, /bin/ping, /sbin/dhclient, /usr/bin/net, /sbin/iptables, /usr/bin/rfcomm, /usr/bin/wvdial, /sbin/iwconfig, /sbin/mii-tool ## Installation and management of software # Cmnd_Alias SOFTWARE = /bin/rpm, /usr/bin/up2date, /usr/bin/yum ## Services # Cmnd_Alias SERVICES = /sbin/service, /sbin/chkconfig, /usr/bin/systemctl start, /usr/bin/systemctl stop, /usr/bin/systemctl reload, /usr/bin/systemctl restart, /usr/bin/systemctl status, /usr/bin/systemctl enable, /usr/bin/systemctl disable ## Updating the locate database # Cmnd_Alias LOCATE = /usr/bin/updatedb ## Storage # Cmnd_Alias STORAGE = /sbin/fdisk, /sbin/sfdisk, /sbin/parted, /sbin/partprobe, /bin/mount, /bin/umount ## Delegating permissions # Cmnd_Alias DELEGATING = /usr/sbin/visudo, /bin/chown, /bin/chmod, /bin/chgrp ## Processes # Cmnd_Alias PROCESSES = /bin/nice, /bin/kill, /usr/bin/kill, /usr/bin/killall ## Drivers # Cmnd_Alias DRIVERS = /sbin/modprobe # Defaults specification # # Refuse to run if unable to disable echo on the tty. Defaults !visiblepw # # Preserving HOME has security implications since many programs # use it when searching for configuration files. Note that HOME # is already set when the the env_reset option is enabled, so # this option is only effective for configurations where either # env_reset is disabled or HOME is present in the env_keep list. # Defaults always_set_home Defaults match_group_by_gid # Prior to version 1.8.15, groups listed in sudoers that were not # found in the system group database were passed to the group # plugin, if any. Starting with 1.8.15, only groups of the form # %:group are resolved via the group plugin by default. # We enable always_query_group_plugin to restore old behavior. # Disable this option for new behavior. Defaults always_query_group_plugin #Defaults env_reset Defaults env_keep = "COLORS DISPLAY HOSTNAME HISTSIZE KDEDIR LS_COLORS" Defaults env_keep += "MAIL PS1 PS2 QTDIR USERNAME LANG LC_ADDRESS LC_CTYPE" Defaults env_keep += "LC_COLLATE LC_IDENTIFICATION LC_MEASUREMENT LC_MESSAGES" Defaults env_keep += "LC_MONETARY LC_NAME LC_NUMERIC LC_PAPER LC_TELEPHONE" Defaults env_keep += "LC_TIME LC_ALL LANGUAGE LINGUAS _XKB_CHARSET XAUTHORITY" # # Adding HOME to env_keep may enable a user to run unrestricted # commands via sudo. # # Defaults env_keep += "HOME" # Defaults secure_path = /sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin Defaults env_keep += "PATH" ## Next comes the main part: which users can run what software on ## which machines (the sudoers file can be shared between multiple ## systems). ## Syntax: ## ## user MACHINE=COMMANDS ## ## The COMMANDS section may have other options added to it. ## ## Allow root to run any commands anywhere root ALL=(ALL) ALL ## Allows members of the 'sys' group to run networking, software, ## service management apps and more. # %sys ALL = NETWORKING, SOFTWARE, SERVICES, STORAGE, DELEGATING, PROCESSES, LOCATE, DRIVERS ## Allows people in group wheel to run all commands %wheel ALL=(ALL) ALL ## Same thing without a password # %wheel ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL ## Allows members of the users group to mount and unmount the ## cdrom as root # %users ALL=/sbin/mount /mnt/cdrom, /sbin/umount /mnt/cdrom ## Allows members of the users group to shutdown this system # %users localhost=/sbin/shutdown -h now ## Read drop-in files from /etc/sudoers.d (the # here does not mean a comment) #includedir /etc/sudoers.d
設定してみたものの、変わらず...
What is buildin command?
何か、
source is a shell builtin, so it cannot be executed without the shell. However, by default, sudo do not run shell. From sudo
https://unix.stackexchange.com/questions/202332/sudo-source-command-not-found
cd is a shell builtin. sudo only works with executables. You could do sudo sh -c 'cd dirname' but as soon as the shell exits, you're returned to the directory you started from. If you say what it is you're trying to accomplish then I can help you find a way to do that.
https://superuser.com/questions/241129/why-wont-sudo-cd-work
⇧ shell buildinって言葉が出てくるんだが...
更に、ググってみたところ、
So, the question, “What is the shell command in Linux” is a bit misleading. There is no actual “shell” command to the best of my knowledge. The usual default shell for command-line is “bash”, which is a newer version of an first shell that was named “bourne shell” and its command line name was “sh”. The “b”, “a” in “bash” stands for “bourne-again.” There are several shells that proceded “sh”.
⇧ Linuxの仕組みな話が出てきて、そもそも、Linuxで用意されているコマンドでは無くて、Shellに組み込まれてるコマンド?ってことになるんかな。(ShellもLinuxを構成してる要素の一部ってことだと思うけども)
で、
⇧ シェルには様々なものがあるからして、利用しているシェルによってbuildinは変わってきそうではありますと。
⇧ 上記サイト様を参考に、「WSL 2(Windows SubSystem for Linux 2)」の「Oracle Linux 8.7」で現在、使用しているシェルでbuildinの一覧を確認してみた。
alias bg bind break builtin caller cd command compgen complete compopt continue declare dirs disown echo enable eval exec exit export false fc fg getopts hash help history jobs kill let local logout mapfile popd printf pushd pwd read readarray readonly return set shift shopt source suspend test times trap true type typeset ulimit umask unalias unset wait
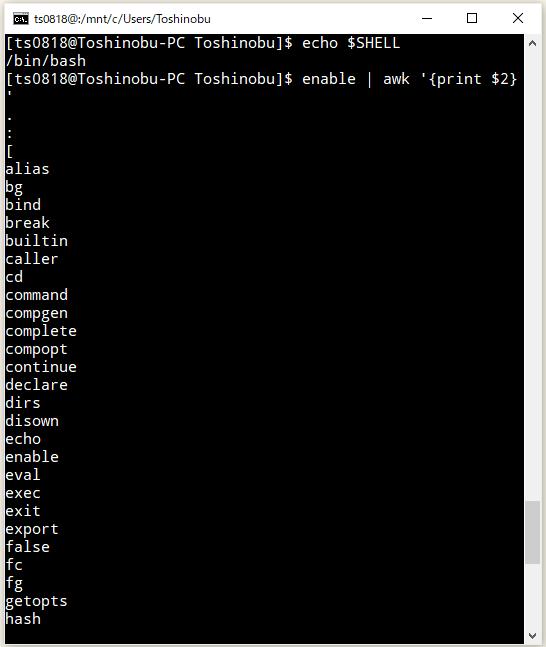
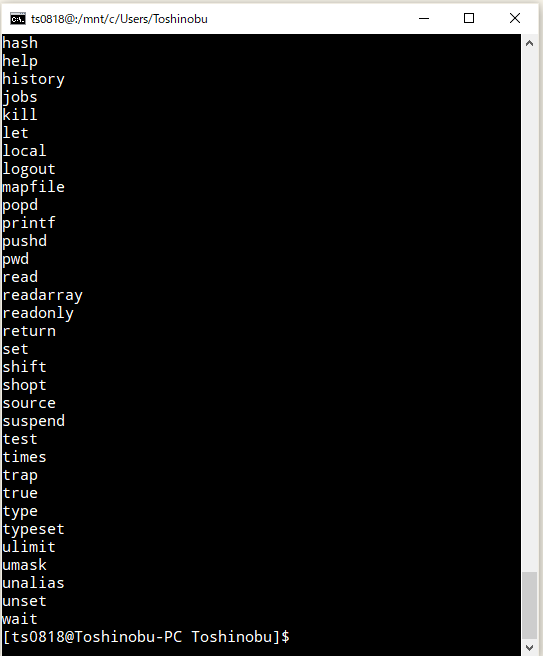
⇧ sourceコマンドおりますと。
で、『sudo: source: command not found』が発生するユーザー(「Oracle Preinstallation RPM」で勝手に追加されたユーザー)で確認してみたところ、
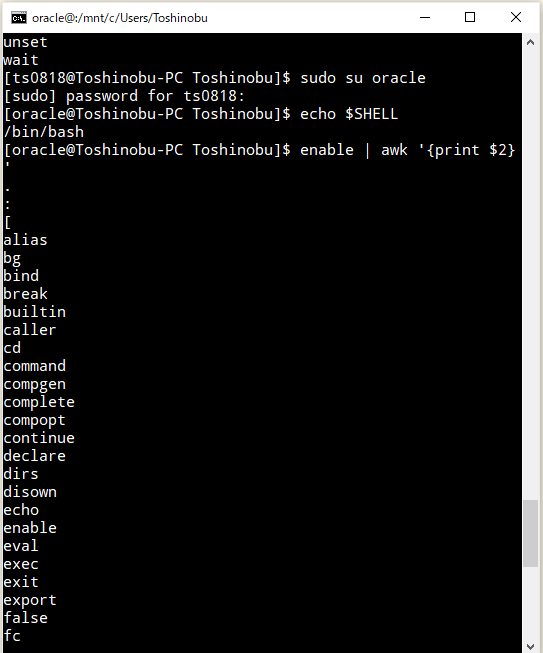
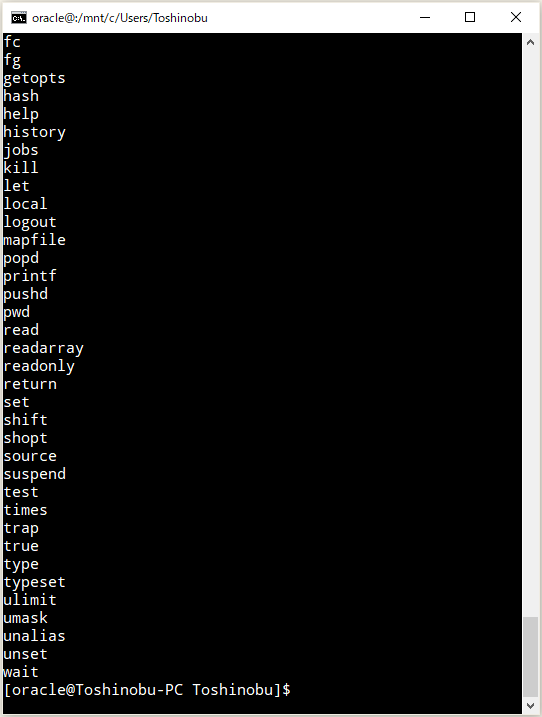
⇧ うん?
普通に、sourceコマンドおるんだが...
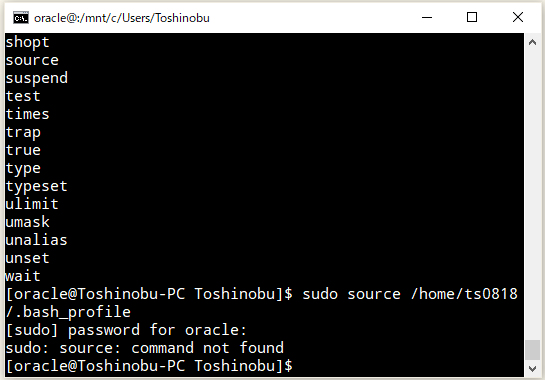
⇧ 何だろう...このエラーメッセージの役立た無さは...
「WSL 2(Windows SubSystem for Linux 2)」に「Oracle Linux 8.7」をインストールした時に作成したデフォルトのユーザーで試してみたところ、
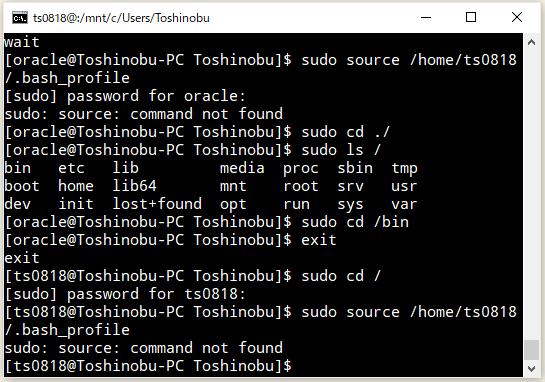
⇧ なるほど、sourceコマンドがあろうが、無かろうが、
sudo [shell buildin]
⇧ 上記のように、sudoでShellのbuildinコマンドを叩くとエラーになるっぽい...
う~む、大人しく、rootユーザー(スーパーユーザー)に切り替えて、実行しろってことなんかね...
毎度モヤモヤ感が半端ない...
今回はこのへんで。

